What compels Philippine enterprises to optimize inventory management in 2025?
The country’s retail market is projected to reach USD 103.28 billion in 2030, reflecting a strong consumer base and heightened competition. This surge is reflected in external trade, with total goods traded rising to USD 17.31 billion in March 2025, representing an annual increase of 9.6%, which demonstrates the growing movement of products through increasingly complex supply chains. Simultaneously, consumer spending hit PHP 4.07 trillion in March 2025, emphasizing the mounting pressure on businesses to balance stock availability with cost efficiency. Together, these trends underscore the pressing need for effective inventory management strategies to prevent losses and maintain profitability.
This blog explores the causes, financial implications, and best practices for managing inventory write-downs, enabling businesses to remain resilient and prepared for market fluctuations.
An inventory write-down occurs when a business reduces the book value of its inventory to reflect its lower market value. This typically happens when inventory becomes obsolete, damaged, or unsellable at its original price. In simpler terms, it means acknowledging that the products you have in stock aren’t worth as much as you thought.
To ensure their financial statements reflect current market realities, businesses must recognize the importance of inventory write-downs. By maintaining accurate inventory records, companies can avoid overstating their assets, which could mislead investors or potential buyers about the actual value of the company. The significance of this is underscored by the changes in inventories in the Philippines, which averaged -5,633.97 million PHP from 2000 to 2025, with fluctuations reaching historic highs of 98,462.12 million PHP in the latter part of this range.
Key Factors Leading to Write-Down:
Several factors can lead to inventory write-downs, including:
Understanding these factors helps you avoid unexpected write-downs and maintain accurate financial records. Next, we’ll take a closer look at how these write-downs affect your financial statements.
Read: How to Track Inventory: Steps and Tips
Inventory value drops affect more than just stock; they impact the entire financial picture. Write-downs can significantly alter the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow, influencing profitability and operational decisions. Understanding these effects is crucial for businesses to manage their operations effectively. Let’s explore how write-downs appear in key financial statements and their implications for operations.
When you write down inventory, it directly impacts your balance sheet. The value of your inventory asset is reduced, which in turn lowers your total assets. This reduction will also affect your equity, as the decrease in inventory value shows a loss to the business.
Inventory write-downs show up as expenses on your income statement. The immediate effect is that your profits will decrease, as you’re recognizing a loss from the reduced inventory value. This is important to understand because it directly impacts your bottom line and profitability.
Even though a write-down doesn’t involve an actual cash outflow (since it’s a non-cash adjustment), it still affects your operating cash flow. The reduction in inventory value may impact how you manage working capital and future spending.
Example:
Let’s say your business has $100,000 worth of inventory. After a market downturn, your inventory is only worth $70,000. The $30,000 write-down will reduce your assets and result in an expense on your income statement. This example illustrates the importance of having a clear understanding of the financial implications of write-downs.
The impact of inventory write-downs stretches beyond just the balance sheet. In the next section, we’ll explore the methods you can use to account for these changes.
There are various inventory write-down methods, each with distinct valuation approaches. Choosing the proper process is crucial, as it influences the frequency and amount of financial adjustments recognized. By understanding these methods, you can effectively manage write-downs in your financial reports and enhance your inventory strategy.
Each of these methods plays a role in determining the financial impact of write-downs on your e-commerce business. Now, this leads us to determine the best ways to record inventory in detail, as it can significantly impact your overall profitability.
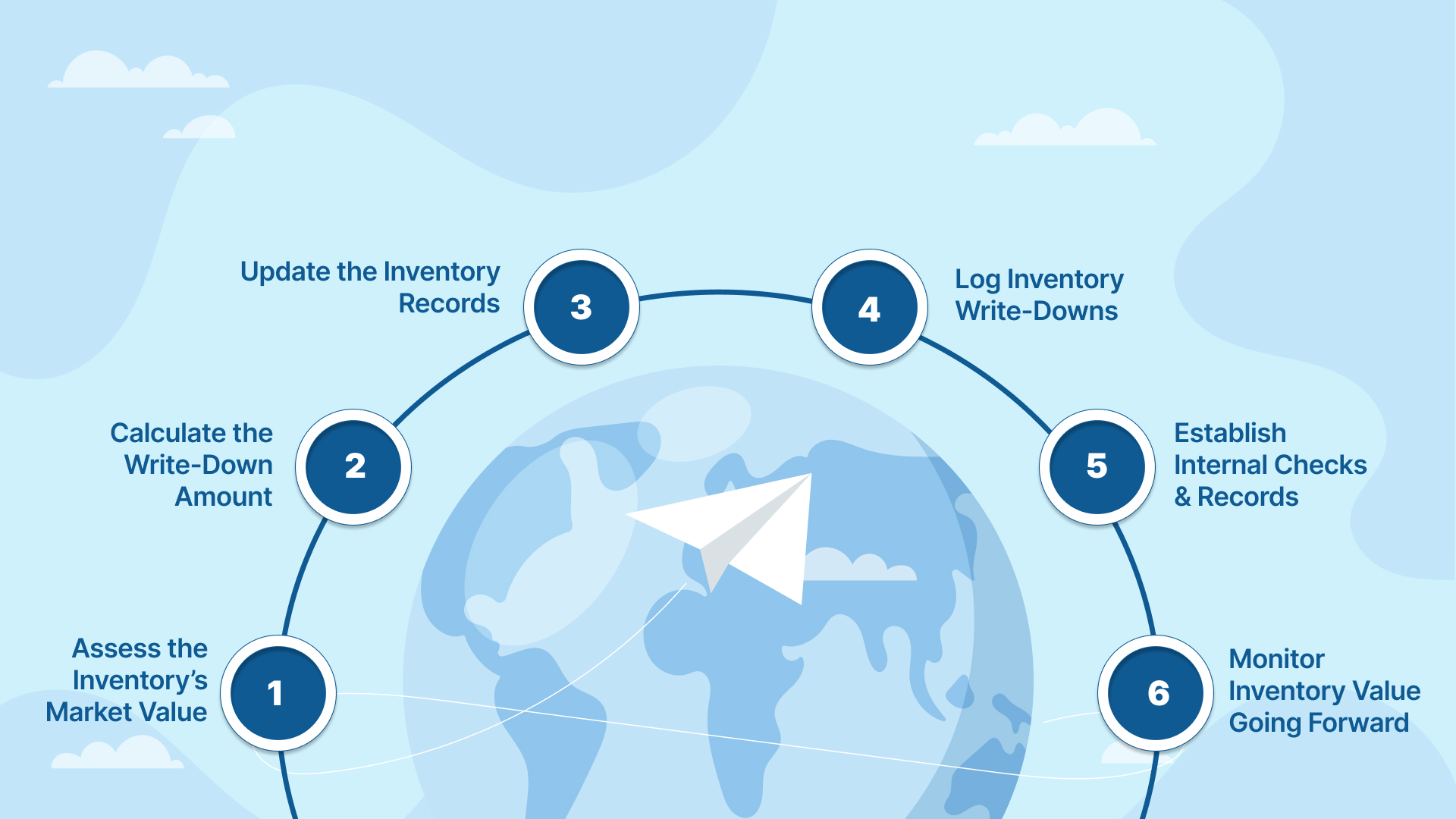
Writing down inventory involves reducing the book value of your stock to reflect its lower market value or net realizable value (NRV). This process is crucial to ensure that your financial statements accurately reflect the current value of your inventory. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly execute an inventory write-down:
The first step in writing down inventory is to assess whether its current market value is lower than the original cost. This can occur for several reasons, including obsolescence, damage, expiration, or market fluctuations.
Once you identify the inventory that needs to be written down, the next step is to calculate the amount of the write-down. The amount will be the difference between the inventory’s original cost and its current market value (or Net Realizable Value, NRV). This calculation ensures that the adjusted inventory value is accurately reflected in the financial statements.
For instance, if you purchased an item for PHP 5,000, but it now has a market value of only PHP 3,500 due to a decline in demand, the write-down would be PHP 1,500.
After calculating the write-down, update your inventory records accordingly. This will reduce the value of the affected inventory on the balance sheet. It’s essential to use a consistent method, such as the Lower of Cost or Market (LCM) method, to ensure that write-downs are applied in accordance with accounting standards.
Once the write-down is finalized, it should be recorded as an expense in the income statement. This recognition of loss helps businesses maintain accurate profit margins and prevent inflated asset values.
Additionally, the reduction in inventory value will be reflected in the balance sheet under the “Current Assets” section, lowering the total value of the inventory.
Ensure that the entire process is well-documented for future audits or regulatory requirements. Maintain proper records of the inventory write-down decisions, including the reasons for the write-down, calculations, and updated inventory levels.
Internal controls, such as periodic inventory audits and regular market assessments, can also help catch issues early and prevent excessive write-downs.
After performing the write-down, it’s crucial to keep monitoring the value of your inventory. This includes tracking the inventory’s recovery or further decline in market value. Suppose the market value of the written-down inventory recovers. In that case, you may be able to reverse the write-down, depending on the accounting standards you’re following (e.g., PFRS in the Philippines).
By following these steps, you can ensure that your inventory is accurately valued and that your financial records reflect the true worth of your assets.
Now that you are familiar with the procedures, let’s examine how inventory write-downs specifically impact e-commerce operations.
Read: Understanding Merchandise Inventory: Essential Guide for Sellers
An inventory write-down affects both finances and e-commerce operations. This section explores the broader implications of write-downs on compliance, transparency, and efficiency.
When your business in the Philippines faces an inventory write-down, it’s essential to comply with local accounting standards and reporting regulations. The Philippines follows the Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRS), which is based on the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Understanding these regulations ensures transparency in reporting inventory losses, helps maintain trust with investors and partners, and prevents potential legal or financial repercussions.
Proper reporting of inventory write-downs is essential for maintaining accurate financial statements and ensuring compliance with Philippine law.
While PFRS is aligned with IFRS, there are notable considerations specific to businesses in the Philippines:
This alignment with IFRS provides a level of flexibility for businesses, particularly those engaged in international trade or expansion. However, it also means that firms in the Philippines must ensure compliance with the specific requirements of the PFRS to maintain consistency and accuracy in their financial reporting.
Transparency is an integral part of reporting inventory write-downs. Philippine regulations require businesses to disclose any significant inventory write-downs in their financial statements, specifically under Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRS) 12, which pertains to the Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities. This includes providing information on the circumstances leading to the write-down, such as the nature of the loss (e.g., obsolescence, decline in market value, damage), and any reversals made during the reporting period.
These disclosures ensure that stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulators, are fully informed about the business’s financial health and asset value. Ensuring accurate and timely reporting also helps prevent potential legal challenges that may arise from misleading financial statements.
This leads us to examine the best practices that can help manage inventory effectively.
Read: Improving Stock Control Systems: Methods and Best Practices
Effective inventory management is crucial for minimizing write-downs and ensuring your business operates smoothly. By adopting efficient techniques, staying proactive, and integrating technology, you can reduce the risks that lead to unnecessary financial adjustments.
Using methods like Just-in-Time (JIT) and ABC analysis not only helps you maintain lean inventory but also aligns it with customer demand. While JIT prevents overstocking by allowing you to purchase stock as needed, ABC analysis prioritizes high-value items, ensuring that you focus on products with the highest turnover. Furthermore, the growing importance of these strategies is underscored by the projection that the supply chain management software market will reach a revenue of USD 40.57 million by 2030.
Regularly reviewing inventory and analyzing market trends helps you identify slow-moving or obsolete products early. By monitoring inventory turnover rates and adjusting stock levels accordingly, you can reduce the chances of holding unsellable goods.
Modern inventory management systems, equipped with real-time data and predictive analytics, enable you to adjust stock levels in response to actual demand. This prevents overstocking and ensures you’re not left with obsolete inventory.
Conducting regular inventory audits ensures that your physical stock matches your digital records. This helps identify discrepancies early and prevents future write-downs by maintaining accurate stock levels.
Building flexible relationships with suppliers enables you to adjust inventory levels in response to actual demand, ensuring optimal stock levels are maintained. Negotiating favorable terms, like lower minimum order quantities, can reduce overstocking risks and help maintain a smooth supply chain.
By following these best practices, you can minimize the likelihood of write-downs and maintain efficient e-commerce operations. Now, let’s examine how to manage an inventory write-down when it occurs.
Even with best practices in place, inventory write-downs can still occur. How you respond to them can make a difference in how your business recovers and thrives. This will help you understand the steps you can take to manage and minimize the impact of write-downs, providing actionable advice tailored to your specific business needs.
By taking swift action with Inspire Solutions and reassessing your strategy, you can recover from an inventory write-down and ensure your business remains on track.
At Inspire Solutions Asia, we understand the complexities of running a successful e-commerce business. Whether you’re just starting or looking to streamline your operations, we provide the tools and services you need to grow efficiently and profitably in the digital marketplace.
Our comprehensive ecosystem provides warehousing and fulfillment, sourcing and importation, financing solutions, and reliable same-day and next-day delivery services – everything your business needs to thrive. With our expertise and technology-driven approach, we simplify operations, reduce costs, and help you scale faster without the headaches.
Partner with Inspire Solutions Asia today, and let us help you focus on what truly matters: growing your business. From flexible financing solutions to seamless logistics and inventory management, we’re here to make your e-commerce journey smooth and successful.
Contact us now to schedule a consultation and discover how we can enhance your e-commerce operations. Let us be the driving force behind your growth.